Zero Trust Domains
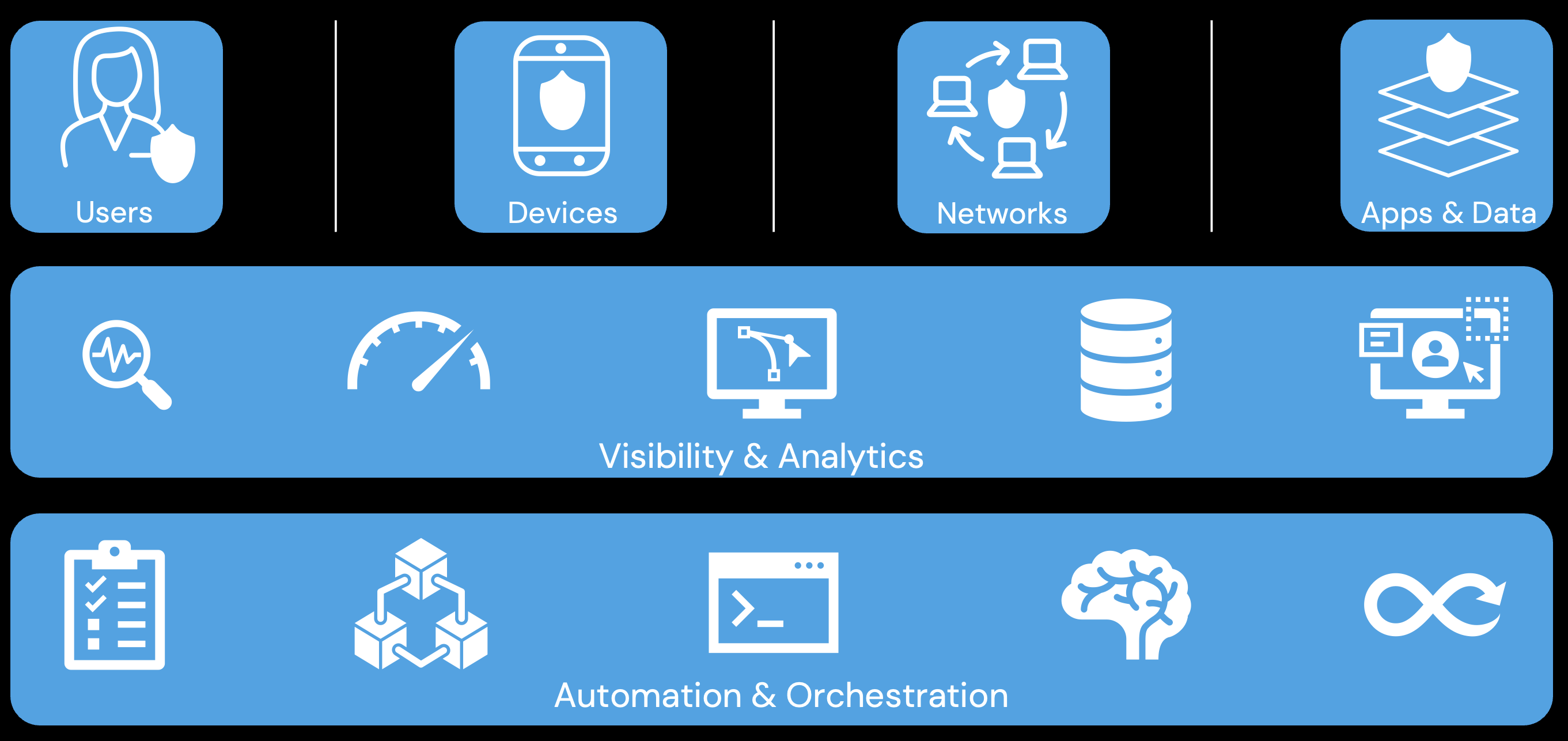
Users
A user is defined by an attribute or set of attributes that describe its identity. Users can represent people (employees, contractors, guests, etc), services, or IoT devices.
When a user requests access to a resource, its identify must be verified - and, ideally, continuously verified - with strong authentication like MFA.
Devices
A device is any hardware that can connect to a network. Devices can be IoT, smartphones and tablets, desktops and laptops, servers, etc. Devices can be owned by an organization, a partner, or BYOD.
For secure access, devices must be monitored to enforce device health and compliance.
Networks
A network is an open communication medium used to transmit data. Networks can be wired or wireless, internal (Intranet) or external (Internet), etc.
Securing a network requires segmenting and controlling it so as to manage internal and external data flows.
Apps & Data
Applications refer to systems, computer programs, and services that run on-premise, or in a cloud environment. Applications represent the interface by which data is consumed.
The application layer, including containers, should be secured and managed. Applications should be securely delivered.
Data is ultimately what security teams want to protect.
Data should be inventoried, categorized, and labeled. Data should be encrypted at rest and in transit. Mechanisms should be deployed to detect possible data exfiltration.
Visbility & Analytics
Successful Zero Trust relies heavily on signal and solution integration. For this reason, organizations should strive for greater visibility into their network.
Visibility provides a better understanding of performance, behavior, and activity across other zero trust pillars. It improves detection of anomalous behavior
Automation & Orchestration
Successful Zero Trust relies heavily on signal and solution integration. For this reason, security automation and orchestration should be adopted.
Automating and orchestrating security processes increases the speed and scale of policy-based actions across the enterprise. It can improve security and decrease response times. It can assist in managing disparate security systems.
Successfully deploying automation and orchestration solutions require defining processes and applying consistent security policy enforcement across all environments in the enterprise.